Climate XChange recently released Recommendations for State-Level Carbon Pollution Pricing, a comprehensive guide to designing legislation or executive branch action to implement either carbon pollution fees or cap-and-trade policies. The guide is accompanied by a Sample Carbon Fee/Tax Legislation and links to relevant sample regulations and laws for cap-and-trade.
The Recommendations are a one-stop source for legislators, policy analysts, and activists deciding what provisions to put in a policy that fits their state or region. We give options for adapting the policy to the particular energy, economic, and political conditions in your area.
Major topics covered include:
- Fees/taxes vs cap-and-trade
- Which sources of GHG emissions should be covered
- Setting the fee/tax rate over time
- Setting the cap level
- How should the revenue be used
- Administrative issues, such as how to ensure that all low-income households get rebates and get them in a timely manner
Deciding which sources of GHG emissions should be covered is a main policy design choice when writing a carbon pollution pricing bill. Each category involves complications unique to your state. Our guidebook provides answers to the main questions, such as:
- Which fossil fuels should be covered by the fee/tax?
- Should methane leakage be included?
- How should biomass and biofuels be handled?
- Should other greenhouse gases be included?
- Should lifecycle emissions be included?
Deciding how to spend the revenues from either a fee or a cap is always a primary issue and there is flexibility in terms of how a state can choose to allocate those funds. Our guidebook goes into these in depth. Possibilities include:
- Invest in clean energy and transportation, particularly for underserved/overburdened communities
- Return money to vulnerable households and businesses
- Just transition for workers and communities who are reliant on fossil fuel energy industries
- Resilience to the impacts of climate change
- Non-climate purposes that are essential to state budgets
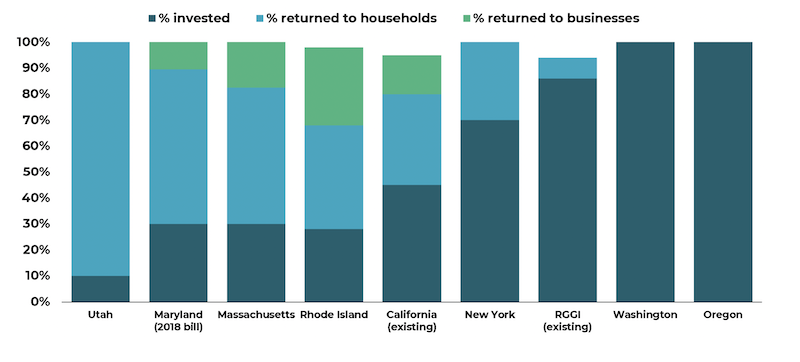
The graph below shows how some proposed legislation and existing cap-and-trade bills choose to spend the funds:
Other important administrative issues to consider when designing a bill are also covered in our guidebook, including:
- Where to collect carbon fees or charge for allowances
- Ensuring that all low-income people get rebates
- Provide rebates on a time schedule that allows people and businesses to pay their bills
- Exempt rebates from being considered in eligibility for other public benefits
- Balance needs to publicize benefits and to keep administrative costs low
- How to administer funds used for clean energy and transportation
For guidance on how to address all these issues refer to the guidebook, to Climate XChange’s other studies, or contact our research staff for a more detailed discussion:
Marc Breslow, Ph.D., Policy and Research Director
Jonah Kurman-Faber, Senior Research Associate